we will explore the secrets behind restful sleep nights at different life stages. And discuss ‘How sleep evolves with Age and How Much It is needed?
Getting restful sleep has become more challenging in our ever-evolving and demanding world. Nevertheless, understanding factors contributing to restful nights is essential for ensuring excellent health and well-being. Sleep is a crucial part of overall health, nutrition, and exercise. It serves as a time for physical refreshment and mental processing of information and emotions. As we navigate through different stages of life, our sleep needs to evolve. Age-related changes in sleep requirements are important when aiming for quality sleep. Managing daily stress becomes essential as it directly affects directly the quality and duration of our sleep can be affected by various factors. Adopting effective stress management techniques ensures that we give ourselves the best chance at achieving restful nights.
Sleep-related issues, such as sleep apnea and insoSleep-related issues like sleep apnea and insomnia, can happen at any point in life. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is important for one’s well-being. It’s vital to understand these concerns and actively seek out appropriate solutions. By proactively addressing these concerns, we can improve our overall well-being and productivity during waking hours. In this section, we will explore the secrets behind restful sleep nights and how sleep evolves at different life stages. We will delve into age-related changes in sleep requirements and provide insights on managing them effectively. Whether you are a young adult struggling with work-related stress or an older individual experiencing shifts in your sleep patterns, this section aims to equip you with valuable knowledge on optimizing your sleep duration and quality.
Read more related this click here.
Sleep Patterns in Infants and Toddlers: Understanding the Developmental Stages and parents awareness
Sleep is very important for a child’s growth, especially when they are young. Knowing about the changes that happen as kids age and sleep can greatly affect their overall health, from babies to toddlers. This part will discuss the different parts of sleep in babies and how their sleep evolves with the change of their age.
One important thing to know about baby sleep is how they fall asleep and wake up. Infants tend to have irregular sleep patterns, falling asleep quickly but awakening often at night. As they get older, the total amount of time they sleep reduces, but their sleep cycles become more regular.
Deep sleep, also called “dreamless sleep,” is important for babies’ growth and development. However, some babies may not sleep well or may have nocturia (frequent urine at night), which can wake them up at night because they can’t get into a deep sleep.
Anxiety and long-term sickness can also make it hard for babies to sleep. Parents should be aware of the early warning signs of insomnia or other sleeping problems in their children and get them the right medical care if they need it. Not getting enough sleep not only hurts the child but can also hurt the parents’ health and how the family works as a whole.
Also, not getting enough sleep or having sleep problems as a baby has been linked to several long-term problems, such as a higher risk of car crashes later in life, a higher chance of developing depression or anxiety disorders, and even problems with thinking and memory because of chronic sleep loss.
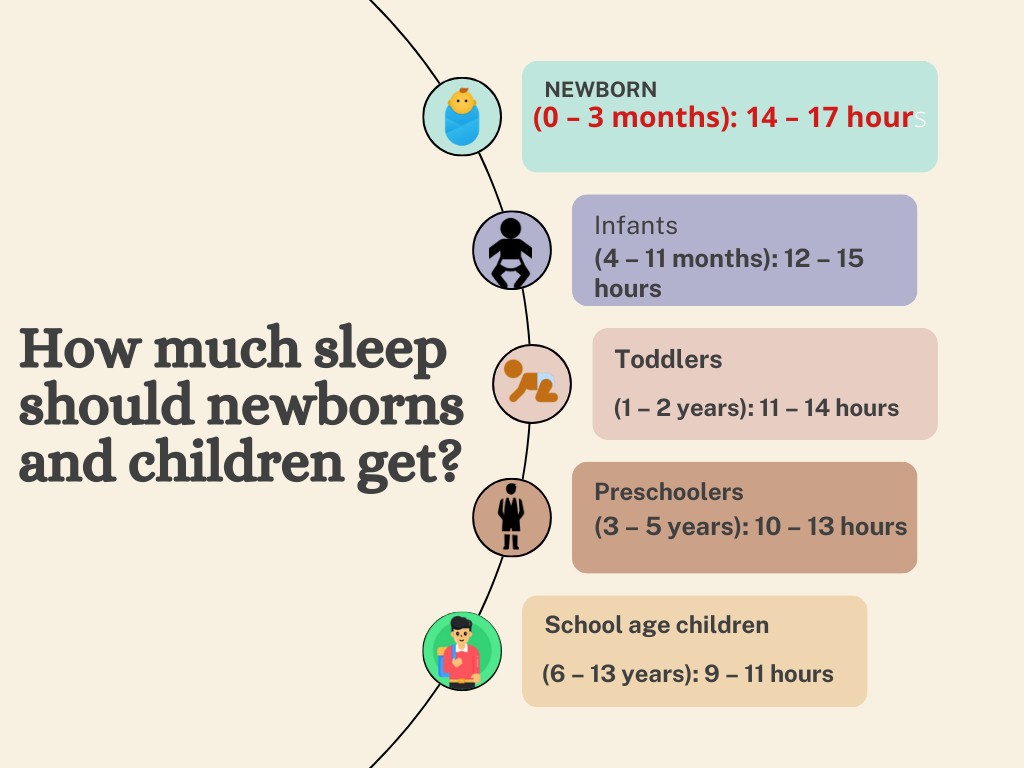
How much sleep should newborns and children get?
- Newborns (0 – 3 months): 14 – 17 hours
- Infants (4 – 11 months): 12 – 15 hours
- Toddlers (1 – 2 years): 11 – 14 hours
- Preschoolers (3 – 5 years): 10 – 13 hours
- School age children (6 – 13 years): 9 – 11 hours
Sleep in Childhood: Exploring the Growing Years

The importance of sleep to everyone’s overall well-being is particularly pronounced for adolescents. Due to the rapid physical and emotional development of teenagers, they are required to sleep between eight and ten hours each night. Unfortunately, most teenagers only sleep 6.5 to 7.5 hours per night on a regular basis. There are several adverse effects associated with sleep deprivation, including impaired cognitive abilities: Sleep deprivation may inhibit a teenager’s ability to concentrate, learn, and retain information. In addition, sleep-deprived teenagers are more likely to experience car accidents and other mishaps. Mental health issues: Sleep deprivation can exacerbate the symptoms of anxiety and depression. An increase in obesity, diabetes, and heart disease is associated with inadequate sleep.
Teenagers can enhance their sleeping habits by establishing a consistent sleep routine. It is important to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Establishing a relaxing bedtime ritual: It is best to avoid screen time an hour or two before sleeping and to engage in relaxing activities such as reading or taking a bath instead. Make sure that the bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool: Darkness promotes the production of melatonin, which is an essential hormone for maintaining sleep patterns. Avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bedtime due to their potential interference with sleep. Taking regular exercise: Regular exercise can improve the quality of sleep; however, strenuous exercise should be avoided close to bedtime.
How much sleep do teenagers need?
- Teenagers (14 – 17 years): 8 – 10 hours
- Younger adults (18 – 25 years): 7 – 9 hours
Sleep in Adulthood: Balancing Responsibilities and Restful Nights

We can often neglect our sleep due to the demands of everyday life, juggling work, family, and social commitments. It is, however, important to recognize that sleep is not merely a luxury but an essential biological requirement for our physical and mental well-being. Adults require seven to eight hours of sleep each night, but many need help to meet this requirement. Inadequate sleep has far-reaching effects, including the impairment of cognitive performance, an increased risk of accidents and injuries, and a worsening of chronic health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
It is vital to balance our responsibilities with sufficient sleep. The following tips will help you to know the sleep evolves and prioritize sleep in adulthood:
- Follow a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends.
- Establish a calming bedtime routine.
- Create a conducive sleeping environment by ensuring darkness, quietness, and a comfortable temperature.
- Refrain from consuming caffeine or alcohol before bed.
- Engage in regular physical activity but refrain from vigorous exercise close to bedtime.
- Effectively manage stress as it has a significant impact on sleep quality.
Whenever you experience persistent sleep problems or suspect that you are having a chronic sleep problem, it is best to seek professional assistance and keep in mind sleep evolves at different ages.
How much sleep do adults need?
- Adults (26 – 64 years): 7 – 9 hours
- Older adults (65+ years): 7 – 8 hours
While these ranges provide general guidance, individual sleep needs may vary. Factors like stress, physical activity, overall health, and sleep quality can influence the amount of sleep you need.
The Role of External Factors on Sleep Quality through the Lifespan
Throughout our lives, various external factors impact our sleep. definitely sleep evolves at different ages. Several factors, such as lifestyle, environment, and societal expectations, can affect the quality and duration of our sleep, ultimately affecting our health. Among the lifestyle habits contributing to daytime fatigue are irregular sleep schedules, excessive caffeine consumption, and late-night screen time. The environment can also interfere with our ability to sleep by disrupting the production of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. Furthermore, societal pressures like demanding work schedules and academic stress can contribute to sleep deprivation. In developed countries, adolescents are more prone to sleep deficits due to academic pressure and technology use late at night. The risk of chronic diseases like obesity, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes increases with sleep deprivation. Moreover, it can impair cognitive function, leading to decreased attention span, memory, and performance issues. Recognizing these external factors influencing sleep for our overall well-being is essential.
Quality sleep is a cornerstone of overall health and well-being, impacting our physical, mental, and emotional functions. Regardless of age, it’s vital to adopt effective sleep habits to ensure optimal sleep duration and quality. Here are some essential strategies for promoting good sleep hygiene and sleep evolves across different age groups:
For Children and Adolescents:
– Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule: By maintaining regular bedtime and wake-up times, the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle can be regulated.
– Develop a Calming Bedtime Routine: Engaging in relaxing activities such as reading or taking a warm bath an hour before bed can help prepare the body for sleep.
– Minimize Screen Time Before Bed: Avoiding electronic devices before bedtime is crucial as the blue light they emit can disrupt the production of melatonin, an important hormone for regulating sleep.
– Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Keeping the bedroom dark, quiet, and cool promotes restful sleep.
– Limit Daytime Napping: While short naps can be beneficial, excessive napping may interfere with nighttime sleep.
For Adults:
– Maintain Consistent Sleep Patterns: Establishing regular sleeping times helps regulate the body’s natural circadian rhythm.
– Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Regular exercise can improve sleep quality; however, avoid intense workouts close to bedtime.
– Minimize Caffeine and Alcohol Intake: Consuming caffeine can disrupt sleep patterns while alcohol may initially aid in falling asleep but later disrupts restful slumber.
– Cultivate a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Prioritize stress-reducing activities before bed to promote relaxation.
By implementing these practices tailored to different age groups, you can support healthy sleeping habits that contribute to overall well-being.
Conclusion: How Sleep Evolves with Age
In conclusion, we come to know sleep evolves and sleep hygiene practices are essential for individuals of all ages to attain and maintain good quality sleep. Children and adolescents benefit from a regular sleep schedule, a relaxing bedtime routine, limiting nap time, and avoiding screen time before bed. Likewise, adults benefit from regular sleep schedules, exercise (while avoiding strenuous workouts close to bedtime), avoiding caffeine, and establishing a relaxing bedtime routine. These strategies can significantly improve sleep quality and duration across different age groups. We must incorporate these practices into our daily routines to promote better health and well-being through improved sleep.

